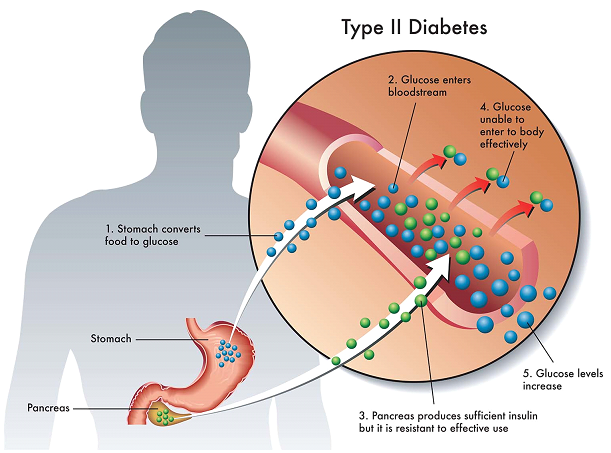
Type 2 Diabetes, a prevalent chronic health condition, significantly impacts individuals globally. It is characterized by the liver's inability to effectively use insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Unlike Type 1 Diabetes, which is often diagnosed in childhood, Type 2 can develop at any age but is most common in adults over 45. The rise in obesity rates has been linked to an increase in Type 2 Diabetes cases, making lifestyle factors a crucial area of focus. This condition is more than just a health issue; it affects individuals' daily lives, requiring continuous management and lifestyle adjustments.
The importance of understanding Type 2 Diabetes cannot be overstated. It's a leading cause of critical health complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and vision problems. Despite these challenges, advancements in medical research and treatment options offer hope and improved quality of life for those affected. By comprehensively understanding the nature of Type 2 Diabetes, individuals can take proactive steps in managing their condition and reducing the risk of complications.
Receiving a diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes can be a life-altering moment, often accompanied by a mix of emotions such as confusion, fear, and uncertainty. It's important to understand that while diabetes is a serious condition, it's also a manageable one. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, such as the A1C test, which measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. A result of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes.
Coming to terms with a chronic condition requires time and support. Education about type-2 diabetes in Denmark, its potential complications, and ways to manage it is critical. It's beneficial to build a supportive healthcare team, including doctors, dietitians, and perhaps a diabetes educator, who can provide guidance and help in developing a personalized management plan.
Mental and emotional support is equally important. Connecting with support groups, either in person or online, can offer a sense of community and shared experience. These groups often provide practical advice, emotional support, and can help in coping with the diagnosis.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes focuses on maintaining blood glucose levels within a target range, which is crucial for preventing complications. This involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Medications, such as metformin, are often prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity or reduce glucose production in the liver. Additionally, some may require insulin therapy.
Lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps regulate blood sugar. Physical activity is equally important; the American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential for understanding how different foods, activities, and medications affect blood sugar. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are necessary to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.
Managing diabetes also includes awareness and management of risk factors for heart disease, as diabetes increases the risk of heart-related issues. Quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol, and taking prescribed medications can mitigate these risks.
Nutrition is a cornerstone of Type 2 Diabetes management. A diet that helps maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range is key. This typically involves reducing refined carbohydrates and sugars, while emphasizing fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Lean proteins and healthy fats are also integral parts of a diabetes-friendly diet.
Understanding the glycemic index (GI) of foods can be beneficial. Foods with a low GI are better for blood sugar control. Meal planning and portion control are essential skills to learn. It's not just about what you eat, but also how much and when. Consistent meal timing and controlled portion sizes can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Involvement of a dietitian or a certified diabetes educator can be invaluable in creating an individualized eating plan. They can provide practical advice, from reading food labels to making healthier food choices, tailored to individual preferences and nutritional needs.
Regular physical activity is a key component in managing Type 2 Diabetes. Exercise helps regulate blood sugar levels, increase insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. In addition to aerobic exercises, incorporating strength training twice a week is advised, as it helps build muscle mass, which can further aid in blood sugar control.
For those new to exercise, starting slowly and gradually increasing intensity is important to prevent injury and ensure consistency. It's also essential to monitor blood sugar levels before and after exercise to understand how different activities affect glucose levels. This can help in tailoring the exercise regimen more effectively.
Physical activity should be a daily routine, but it doesn't have to be strenuous or time-consuming. Simple activities like taking the stairs, gardening, or short walks can make a significant difference. It’s about finding enjoyable activities that can be integrated into daily life.
Remember, before starting any new exercise regimen, consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial, especially for those with existing health concerns.
Living with Type 2 Diabetes means making daily choices that directly affect one's health. It requires careful management in various aspects of life, including work, travel, and social events. For instance, at work, it might involve planning meals, managing stress, and ensuring regular movement. During travel, maintaining medication schedules and meal planning becomes crucial.
Social gatherings often revolve around food, which can be challenging. Developing strategies to make healthy choices, like eating a small, balanced meal before attending a party, can help maintain blood sugar levels.
Emotional well-being is just as important as physical health. Stress can affect blood glucose levels, so finding effective ways to manage stress is essential. Techniques like mindfulness, yoga, or even simple breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Building a support system, whether through family, friends, or diabetes support groups, can provide emotional and practical support. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges can be comforting and empowering.
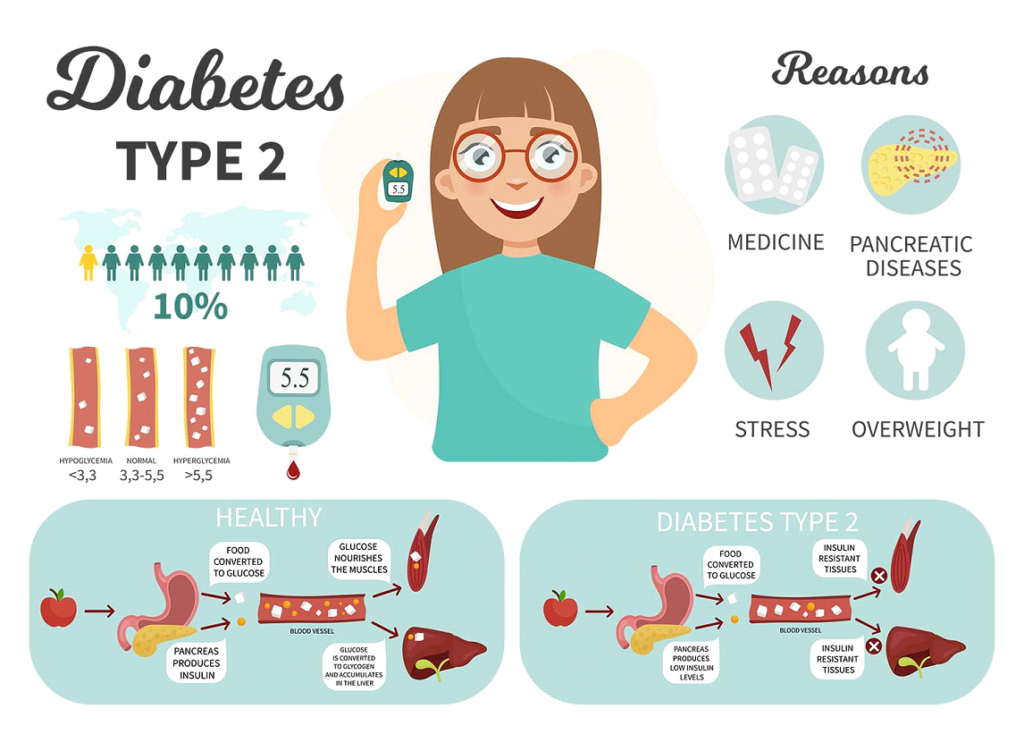
Managing Type 2 Diabetes effectively is crucial to prevent long-term complications. Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, vision problems, and nerve damage. Regular health check-ups are important to monitor for signs of these complications.
Diabetic retinopathy, a common complication affecting the eyes, can lead to vision loss if not managed early. Kidney disease, another complication, may require dialysis if it progresses. Diabetic neuropathy, affecting nerves, can lead to loss of sensation, especially in the feet, increasing the risk of injury.
It's essential for individuals with diabetes to manage their blood pressure and cholesterol levels, as diabetes increases the risk of heart disease. Regular foot care, including inspections and proper footwear, is also important to prevent foot ulcers and infections.
Adhering to medication, maintaining a healthy diet and exercise regimen, and regular monitoring can significantly reduce the risk of these complications.
Finding support while managing Type 2 Diabetes is crucial for both emotional well-being and practical management. Diabetes support groups offer a platform for sharing experiences and tips, providing a sense of community and understanding. These groups can be found in many communities and online, offering diverse perspectives and coping strategies.
Resources for diabetes education are widely available. The American Diabetes Association, for instance, offers extensive educational materials and programs. These resources cover various aspects of living with diabetes, including diet, exercise, medication management, and dealing with emotional challenges.
Engaging with online forums and social media groups dedicated to diabetes can also be beneficial. They provide a platform for asking questions, sharing successes, and receiving encouragement from others who understand the challenges of living with diabetes.
These sites offer a wealth of information for those looking to understand and manage Type 2 Diabetes more effectively.
⦁ American Diabetes Association (ADA): Offers comprehensive information on diabetes management, nutrition, exercise, and community support. ⦁ Visit ADA
⦁ Steno Diabetes Center (SDC): Provides detailed educational resources on diabetes, its complications, and management strategies, and data on diabetes in Denmark. ⦁ Visit SDC
⦁ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - Diabetes Home: Features a wide range of information on diabetes management, & prevention strategies. Visit CDC Diabetes Home
Living with Type 2 Diabetes involves adapting to a new way of life, encompassing changes in diet, exercise, and overall lifestyle. It's important to recognize that while diabetes is a significant part of life, it doesn't define one's identity. Embracing this new normal means understanding and accepting the condition while also acknowledging the strength and resilience it takes to manage it every day.
The journey with diabetes is ongoing and often challenging, but it's also filled with opportunities for personal growth and health improvement. Every step taken towards better health is a victory, whether it's making a healthier meal choice, taking a walk, or successfully managing blood sugar levels.
Our goal is to provide understanding, support, and practical tips for those living with Type 2 Diabetes. It's a journey that doesn't have to be walked alone. There are communities, healthcare professionals, and resources available to help navigate this path.
Remember, living with Type 2 Diabetes is a continuous learning process, and with the right tools and support, anyone can lead a fulfilling and healthy life.

If you or someone you know is living with Type 2 Diabetes, consider exploring the opportunity to participate in clinical trials. These trials are essential for advancing medical research and treatment options. By participating, you not only contribute to the broader understanding of diabetes management but also might gain access to new treatments and personalized care. Additionally, engaging with the diabetes community can offer support, shared experiences, and valuable information. It's a chance to connect with others who understand your journey and to contribute meaningfully to the diabetes conversation. If this interests you, we encourage you to explore these opportunities further. Your involvement could make a significant difference in the world of diabetes care and research.
Sources:
⦁ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), American Diabetes Association (ADA)] ⦁ CDC - Type 2 Diabetes
⦁ American Diabetes Association (ADA), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)] - ⦁ Diabetes Overview
⦁ American Diabetes Association (ADA), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)] – ⦁ Risk Prevention